- Work Hours : Mon to Sat : 09:30- 18:30
3D-Printed Models in the Medical Field:
Diagnostic and Surgical Applications
- Designed by Zoriox Innovation Labs ,Marketed by Graft3D Healthcare Solutions
Overview
3D printing is revolutionizing healthcare by converting digital images into physical, patient-specific anatomical models. These models are crucial resources for clinicians and patients, as they improve diagnostic precision, preoperative planning and surgical performance. They are used in a wide variety of disciplines, such as orthopaedic surgery, neurosurgery, maxillofacial surgery, cardiology, plastic surgery and oncology. 3D printed models are making a real difference in the way complex medical conditions are comprehended and treated.
Diagnostic Applications
Orthopedics
- Thorough assessment of complex fractures, congenital deformities and skeletal deformities.
- Enhanced appreciation of joint pathology before arthroplasty.
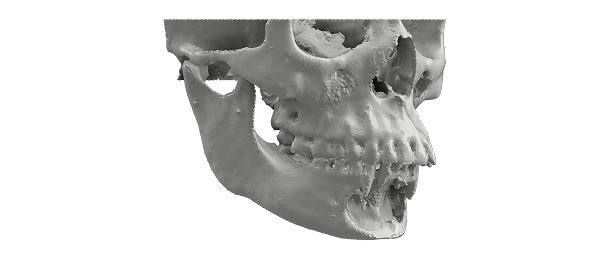
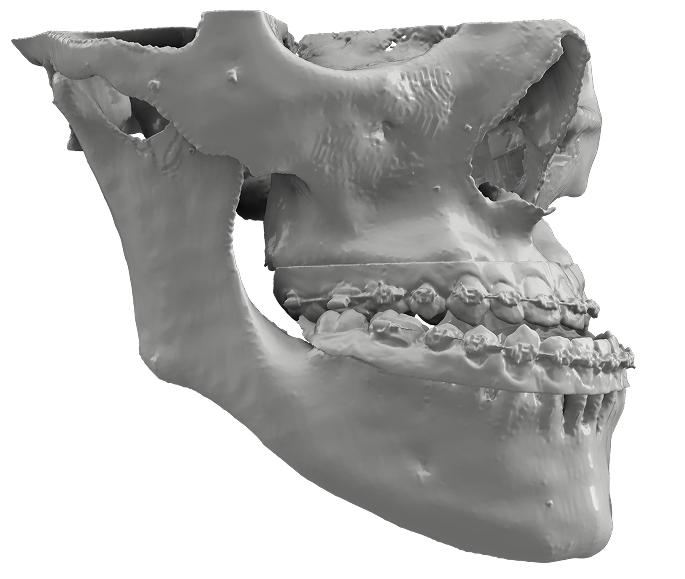
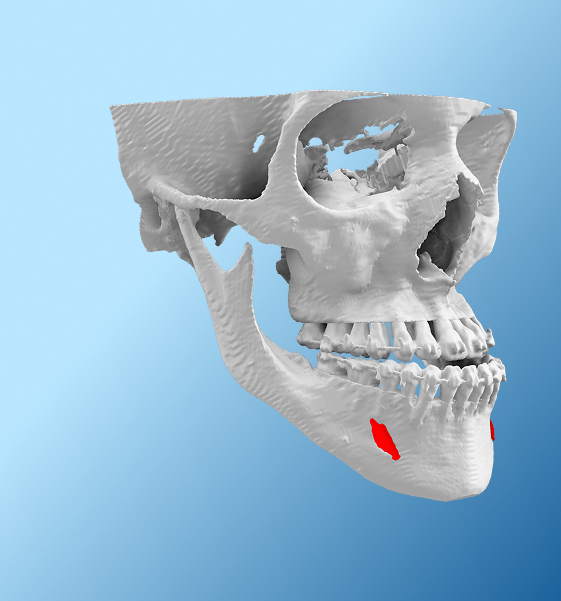
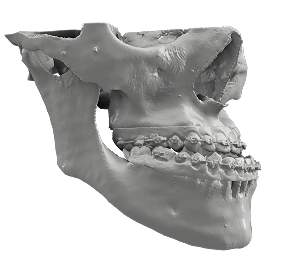
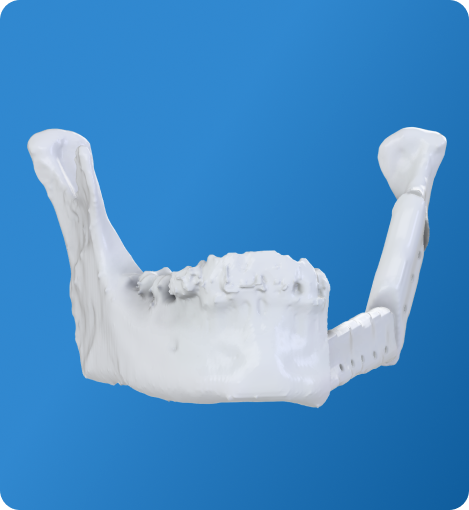
Maxillofacial & Dental
- Visualization of craniofacial deformities, malocclusion or tumours of the jaw.
- Improved patient understanding for orthognathic surgery and dental implant treatment planning.
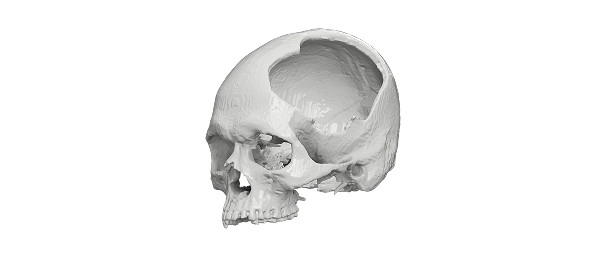
Neurosurgery
- Evaluation of the skull base tumors, aneurysms and congenital malformations of the brain.
- Multiple intricate vascular structures are mapped for accurate diagnosis.
Cardiology
- Pediatric heart defects are demonstrated by patient-specific 3D heart models.
- Increased diagnostic refinement in congenital heart diseases for therapeutic decisions.
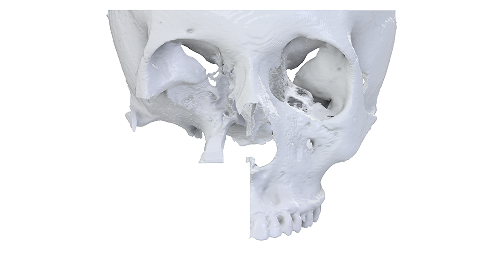
Oncology
- Proper documentation of the size, margins and tumoral extent in relation to adjacent structures.
- Useful in the multidisciplinary tumor board review and for assessing surgical feasibility.
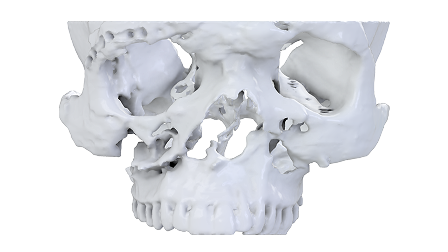
ENT & Head-Neck
- Excellent visualization of complicated sinus and skull base anatomy.
- Diagnostic aid for congenital tracheobronchial anomalies and structural abnormalities.
Surgical Applications
Orthopedics
- Preoperative practice for fracture reduction and deformity correction.
- Personalized surgical guides for joint replacement, spinal deformity correction and bone lengthening.
Maxillofacial & Dental
- Resection of maxilla and mandible with free fibula flap reconstruction.
- Patient-specific implant and fixative plate design and manufacturing.
- Accurate aids for dental implant positioning and orthognathic surgery.
Neurosurgery
- Preoperative mapping for skull base and intracranial tumors.
- Customised cranial implants for cranioplasty.
Cardiac & Vascular Surgery
- Predictive modelling for surgical rehearsal in congenital heart defect and valve repair.
- Pre-operative evaluation for intricate vascular grafting, stent deployment and bypass surgery.
Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery
- Personalized planning of craniofacial repair after trauma or congenital malformations.
- Surgical template design for sculpting deformities, flaps and soft tissue.
ENT & Head-Neck
- Planning for resection and reconstruction in head and neck cancer surgery.
- Individual templates for reconstruction of the trachea and larynx.
General & Oncologic Surgery
- Anatomic models for planning hepatic and renal tumor resections.
- Donor recipient mapping in complex organ transplant procedures.
3D printed anatomical models showcase their broad utility across all disciplines within healthcare. In diagnostic imaging, they enhance insight, communication and patient involvement. For surgeons, they allow personalized preoperative planning and rehearsal as well as increased accuracy during surgical procedures. 3D printing along with developments such as artificial intelligence, augmented reality, virtual reality and bioprinting, improved the opportunities to provide personalized treatments. These methods improve diagnosis and treatment, but also lay the groundwork for the next generation of patient-centered care.
1) What are 3D printed anatomical models in the medical field?
3D printed anatomical models in the medical field are physical replicas of patient anatomy used for surgical planning, training, and communication. They improve understanding of complex structures and help clinicians rehearse procedures before operating.
2) What do 3D printing services for medical professionals typically offer?
3D printing services for medical professionals usually include scanning, image-to-CAD conversion, and production of patient-specific models or guides. These services help hospitals and clinics visualize anatomy and reduce uncertainty before clinical interventions.
3) Why are patient-specific 3D medical models beneficial?
Patient-specific 3D medical models are tailored to an individual’s CT/MRI data, offering precise geometry for planning complex cases. This personalization enhances surgeon confidence, supports patient education, and aids multidisciplinary case discussions.
4) How can I order custom surgical 3D models for hospitals?
To order custom surgical 3D models for hospitals, you typically provide imaging data (like CT/MRI scans), clinical indications, and timelines. Providers convert these scans into printable files, review with clinicians, and then print models for planned procedures.
5) What do medical 3D printing services for hospitals include?
Medical 3D printing services for hospitals include converting imaging into 3D models, printing anatomical parts, and sometimes post-processing and packaging. Some providers also assist in digital planning, training, and materials tailored to clinical needs.
6) How can a 3D printed surgical models provider support operating teams?
A 3D printed surgical models provider supports operating teams by delivering accurate physical replicas that help visualize anatomy, plan cuts or resections, and simulate implant fit. These models help reduce surprises and improve confidence in complex surgeries.
7) What is 3D printing for diagnostic models used for?
3D printing for diagnostic models produces physical anatomy representations that help radiologists, surgeons, and care teams better assess disease extent. They add tactile insight to imaging data, supporting more informed decisions before interventions.
8) Why is 3D printing in healthcare becoming more common?
3D printing in healthcare is becoming more common because it supports precision medicine, personalized treatment planning, and patient education. It also reduces lead times for custom parts and enhances collaborative decision-making across care teams.
9) What are medical 3D printed prototypes and how are they used?
Medical 3D printed prototypes are early physical models of implants, guides, or devices used for fit checking and iterative design. They help engineers and surgeons validate concepts before final production and clinical use.
10) What does 3D printed patient anatomy help clinicians understand?
3D printed patient anatomy gives surgeons and care teams a tangible reference of internal structures, improving spatial understanding beyond flat imaging. This aids surgical planning, enhances teaching, and improves patient communication about procedures.
Contact Us & Get details for
3D-Printed Models in the Medical Field:
Diagnostic and Surgical Applications
