Healthcare 3D printed products
FAQs
What are Healthcare 3D printed products and why do hospitals use them?
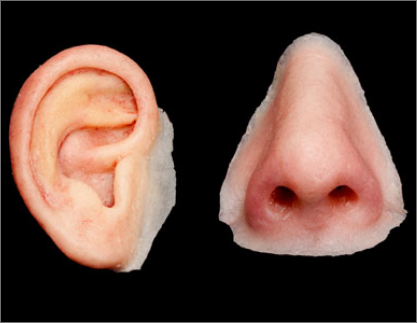
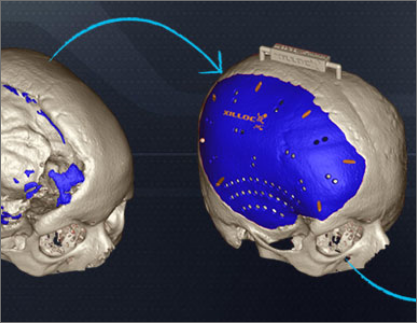
Healthcare 3D printed products include anatomical models, surgical guides, prosthetic/orthotic components, and education tools made from patient or reference data. They help improve visualization, planning accuracy, and communication while reducing iteration time for complex procedures.
How do I choose reliable medical 3D printing companies in India for my hospital?
Evaluate medical 3d printing companies in India on clinical understanding, data handling process, quality checks, material traceability, lead times, and case experience. Prefer teams that support surgeons with design reviews and provide documentation for repeatable outcomes.
What types of 3d printed medical devices are commonly created today?
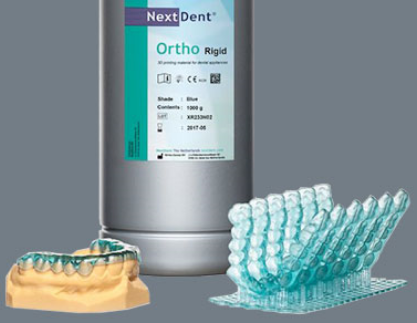
3D printed medical devices often include patient-specific guides, splints, orthoses, prosthetic parts, and customized components for procedural support. The best use cases are those requiring personalization, faster prototyping, and consistent repeat production with controlled specifications.
Are 3d printed surgical instruments safe and practical for routine use?
3d printed surgical instruments can be practical for specific use cases like prototypes, handles, or non-critical tools, depending on material and sterilization compatibility. For clinical adoption, validate strength, biocompatibility, sterilization method, and regulatory requirements.
What should be included in medical 3D printing packages for healthcare teams?
Medical 3D printing packages usually combine hardware, software, training, workflows, and support for converting CT/MRI data into printable designs. A strong package also includes SOPs, quality checkpoints, and ongoing optimization to ensure consistent clinical output.