- Work Hours : Mon to Sat : 09:30- 18:30
3D Printing in Orbital Reconstruction

- Designed by Zoriox Innovation Labs ,Marketed by Graft3D Healthcare Solutions
Overview
The orbital reconstruction is one of the most challenging areas in maxillofacial surgery because of its complex anatomy and location related to critical structures such as the globe and optic nerve. Functional recovery and aesthetic balance are important surgical aims. Conventional reconstruction using premade plates and meshes need much intraoperative bending and contouring, which results in inappropriate orbital volume restoration and asymmetry.
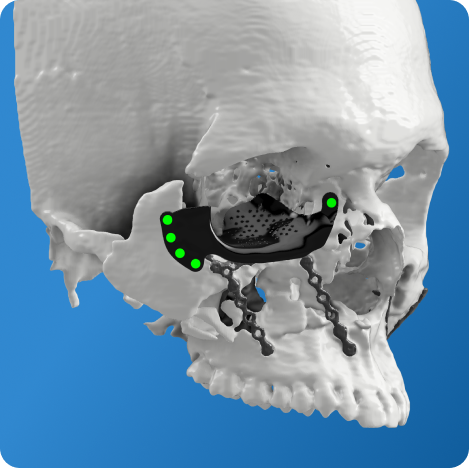
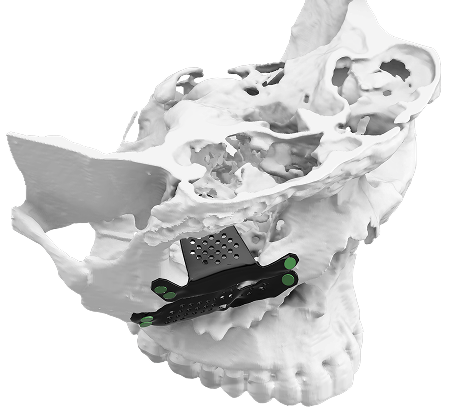
The practice of orbital reconstruction has been revolutionized with the advent of patient specific 3D-printed orbital implants. Individualized implants provide unparalleled accuracy, superior aesthetic results and reproducible outcomes. This has made 3D-printing a gold standard treatment in the field of orbital reconstruction.
Indications for Patient Specific Orbital Implants
- Orbital fractures: In cases of correction of the orbital floor defects, medial or lateral wall and blow-out fracture.
- Secondary deformity reduction: Treatment of enophthalmos, hypoglobus and asymmetry post healing of the fracture.
- Congenital craniofacial diseases: Orbital reconstruction in conditions like crouzon syndrome and treacher collins syndromes.
- Oncologic resection: Orbital volume restoration post tumor removal.
Role of 3D Printing in Orbital Reconstruction
- High resolution CT scanning provides an accurate three dimensional virtual model of the orbit.
- Digital reflection of the normal orbit assists in recreating anatomy.
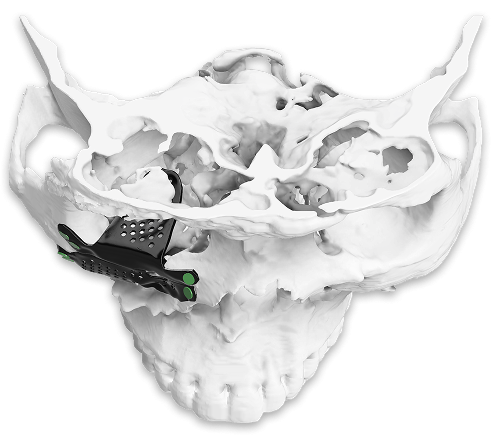
- Custom design of the orbital implant makes possible reconstruction of the orbital floor, medial wall and lateral wall with accuracy.
- 3D printing creates implants of precise curvature, thickness, and contour to restore orbit volume accurately.
- 3D printing in orbital reconstruction provides more surgical precision with less operative time, better function and aesthetics.
Benefits of 3D Printing in Orbital Surgery
- Custom fit: Customized orbital implants accurately mimic the patient's orbital anatomy.
- Symmetry restoration: The globe and orbit are correctly balanced with digital mirroring.
- Reduced surgical time: No need for intraoperative bending or adjusting during the orbital surgery.
- Functional recovery : Useful for improving diplopia, enophthalmos and the malposition of the eye.
- Cosmetic results: Provides a natural, lifted appearance and facial symmetry.

Materials in 3D Printing Orbital Implants
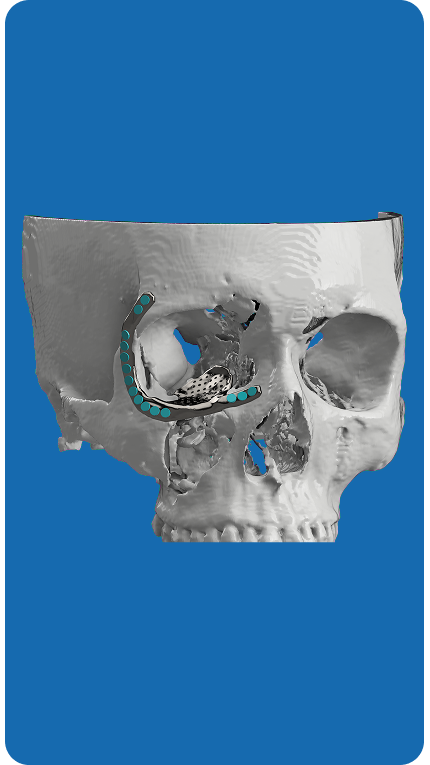
Titanium 3D Printed Implants
- Useful in large or weight bearing orbital wall defects.
- Offer excellent strength, lasting durability and long term stability.
- The porous structure of the titanium promotes the integration of tissue and inhibits migration of the implant.
- Limitation: May produce imaging artifacts on CT/MRI.
Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) 3D Printed Implants
- Light, radio translucent and biomechanically resemble the bone.
- Ideal for cosmetically sensitive orbital reconstruction when postoperative imaging is essential.
- Concave-convex surface increases friction force for a perfect fit and natural shape.
- Limitations: Lower osseointegration than titanium implants.
Future Trends in Orbital Reconstruction with 3D Printing
- Hybrid orbital implants: Titanium mesh with PEEK for strength and aesthetics.
- AI and AR/VR Reinforcement: Real time surgery navigation and AI assisted surgical planning for precision.
- Bioactive scaffolds: Manufacturing of regenerating 3D printed orbital implants promotes faster bone healing and symmetry.
The 3D printing in orbital reconstruction has changed the paradigm in maxillofacial surgery. Custom orbital implants like titanium and PEEK are allowing surgeons to achieve more accurate, symmetric and superior patient outcomes. In the future, hybrid orbital implant designs, AI assisted surgical planning and regenerative biomaterials will further drive coordinating function competence with excellent cosmetic results in the orbital reconstruction.
FAQs
What is orbital reconstruction and when is it clinically indicated?
Orbital reconstruction is required to restore the bony orbit after trauma, tumour resection, infection, or congenital deformity. The primary goals are accurate orbital volume restoration, globe support, and prevention of functional complications such as diplopia and enophthalmos.
How do 3D printed orbital reconstruction models support surgical planning?
3D printed orbital reconstruction models provide a tangible, patient-accurate representation of orbital defects. These models help surgeons assess defect size, plan implant positioning, and evaluate symmetry before surgery, improving intraoperative accuracy.
What are the benefits of patient-specific and custom orbital implants?
Patient-specific and custom orbital implants are designed directly from CT data, ensuring precise anatomical fit. This reduces intraoperative contouring, improves orbital volume restoration, and leads to more predictable functional and aesthetic outcomes.
When are titanium orbital implants preferred?
Titanium orbital implants are preferred in cases requiring high mechanical strength, long-term stability, or reconstruction of large or multi-wall defects. Titanium offers excellent biocompatibility and is commonly used in complex orbital reconstruction scenarios.
What are the clinical advantages of PEEK orbital implants?
PEEK orbital implants are lightweight, radiolucent, and have an elastic modulus closer to bone. These properties allow improved postoperative imaging assessment and precise anatomical reconstruction, making PEEK suitable for patient-specific orbital reconstruction.
How do 3D printed orbital implants improve hospital workflows?
3D printed orbital implants enable preoperative planning and accurate implant fabrication, reducing surgical time and intraoperative adjustments. This supports efficient orbital reconstruction solutions for hospitals and improves consistency in clinical outcomes.
What should hospitals consider when selecting orbital reconstruction services?
Hospitals should evaluate orbital reconstruction services based on clinical expertise, availability of 3D printed orbital implants, material options such as titanium and PEEK, regulatory compliance, and collaboration with the surgical team throughout planning and execution.